Rabies in a postpandemic world: resilient reservoirs, redoubtable riposte, recurrent roadblocks, and resolute recidivism Rupprecht, C.E., Mshelbwala, P.P., Reeves, R.G., Kuzmin, I.V. 2023 Animal Diseases, 3(1), art. no. 15.
Rabies


Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is a highly infectious viral disease that affects cloven-hooved animals, including cattle, sheep and pigs.
SHARE
Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD)
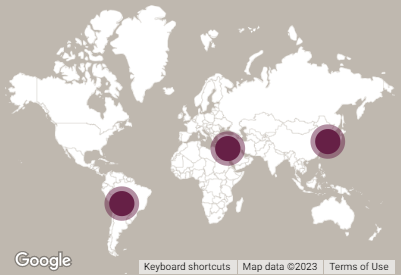
FMD is endemic in various parts of the world, whilst others are FMD-free (e.g. Europe and North America) or working towards eradication (e.g. South America). Find out where the latest reported outbreaks are with this map.
KEY FACTS

Disease Classification
FMD is caused by a virus (Family Picornaviridae) which frequently mutates and is grouped in 7 different and distinct serotypes1– O, A, C, Asia1, SAT1, SAT2, and SAT3. These serotypes are not distributed evenly around the world, for instance the SAT serotypes rarely spread outside of Africa (SAT stands for Southern African Territories). In addition, serotype C has not been identified anywhere since 2004. 1Foot-and-mouth disease: past, present and future, SM Jamal, GJ Belsham, 2013, Vet Res 44, 116

Transmission
The FMD virus is highly contagious, and animals usually become infected by inhaling the virus from the air or ingesting it with their food. There are differences between species in terms of the likely route of infection and the amount of virus needed to cause infection. For example, cattle are more likely to be infected by inhalation whereas pigs are more likely to be infected by ingestion. (Adapted from EuFMD Emergency Preparedness e-learning Course)

Vaccine
Vaccination is an important tool in the control of FMD. As the FMD virus is constantly evolving it is almost impossible to have a vaccine strain that has been developed from a current outbreak (it normally takes 6-18 months to develop new strains). Whilst infection with one serotype does not provide immunity against another serotype, by understanding the topotype and lineage of the outbreak it is possible to select a vaccine strain that is closely related and therefore much more likely to provide protection. This is further enhanced by choosing high potency vaccines, over 6PD50, as these generally provide better cross-protection. High quality vaccines should always be used.
Clinical Signs
FMD is a very painful disease that causes blisters and sores on feet, in the mouth and on teats. Other clinical signs include fever, depression, anorexia, lower milk production, salivation, lameness and abortion. There are differences in clinical signs between affected species.
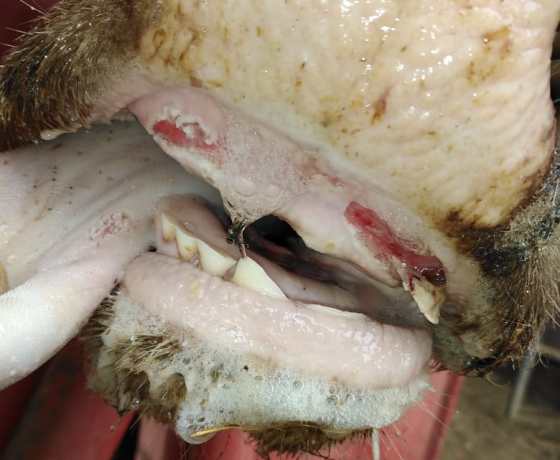
FMD is very painful and causes salivation and loss of appetite. Photo Dr Shaun Morris
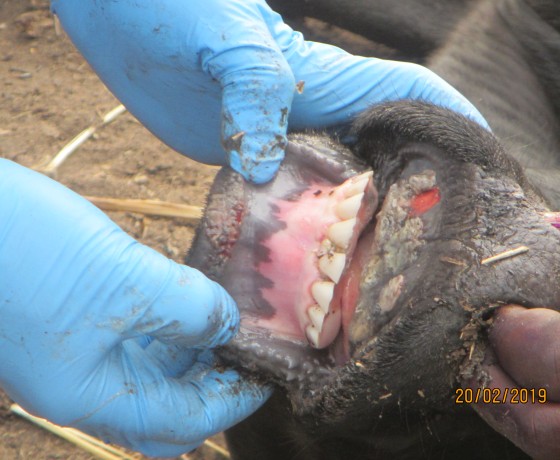
Classical signs of disease include blisters and sores on feet, in the mouth and on teats. Photo by Eufmd.
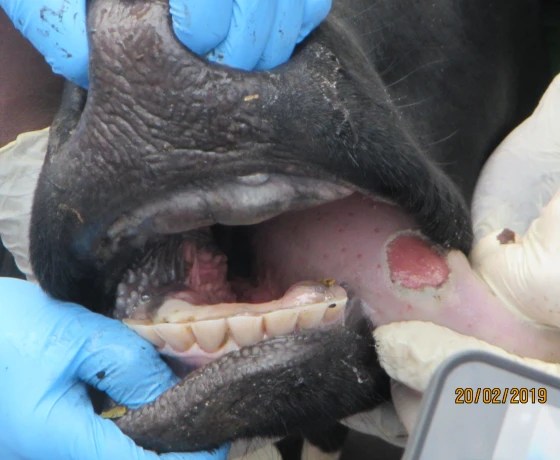
Lesions change in appearance over time which enables lesion aging to determine disease timelines. Photo by Eufmd.
Treatment
As a viral disease, there is no specific and effective treatment for FMD-infected animals. Control and prevention methods, such as biosecurity, vaccination and movement restrictions are important.
Management
Biosecurity is critical in the control and prevention of FMD. This is because the FMD virus is very contagious, which is because it is very persistent in the environment, only requires small amounts to infect animals, and is produced in large amounts by those that become infected. Prompt reporting of possible outbreaks and animal movement restrictions are also important in stopping the spread of FMD.

FOCUS ON…
Focus On… Tracking the movement of livestock – developing strategic interventions for infectious disease control in East Africa
Latest Articles and Events
Knowledge Hub
Innovating at EuFMD OS22
After so long since the last in-person event, it was wonderful to be able to…
Guide – Australia’s DAFF and CSIRO…
A field guide for veterinarians providing information on emergenc
International Symposium of..
My name is Rachel Herschman and I have been an intern on the..
Website – IVVN – International..
The IVVN is an international community of over 1,600 members working togeth…
Boosting disease control with…
Disease control is about a lot more than simply the right vaccine. Building…
Focus On… African Swine Fever (ASF)…
African swine fever (ASF) is present in more than 50 countries on five continent…
Exploring New Frontiers in Anim...
I’m a final year DPhil student studying at The Pirbright Institute and the..
Website – IVVN – International..
Latest Scientific Papers
Rabies
Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD)
Avian Influenza (AI)
No items to show.
Rabies
Avian Influenza (AI)
Rabies
No items to show.
Subscribe to our free newsletter and stay up to date with all news and events.